The world of nanotechnology and materials science is continually evolving, with microscopic particles taking center stage in groundbreaking research and applications.
Understanding PMMA
Nanoparticles:
- Size and Uniformity: PMMA nanoparticles,
with diameters typically in the nanometer range, exhibit precise size and
uniformity, essential for consistent behavior in various applications.
- Optical Clarity: Poly(Methyl
Methacrylate) is transparent, making the nanoparticles ideal for optical
applications and enhancing their use in fields like imaging and
diagnostics.
- Customizable Surface: The surface of this
nanoparticles can be modified with functional groups, allowing for
tailored interactions with different materials.
Applications:
- Biomedical Imaging: The PMMA nanoparticles find applications in imaging technologies, such as
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and fluorescence imaging, contributing to
advancements in medical diagnostics.
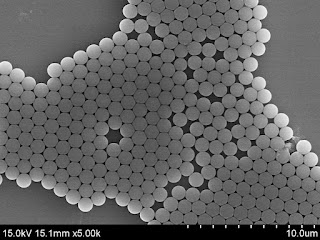
PMMA Nanoparticles - Drug Delivery: The small size and
customizable surface properties of this nanoparticles make them promising
candidates for drug delivery systems, enabling targeted and controlled
release of therapeutic agents.
- Optical Devices: Due to their optical
clarity, these nanoparticles are utilized in the development of optical
devices, including sensors and displays.
Exploring the properties of
Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Microspheres:
- Sphericity and Size Range: PMMA microspheres
boast high sphericity and a range of sizes, providing versatility for
various applications, including calibration standards and research
purposes.
- Density and Buoyancy: The Poly(Methyl
Methacrylate) Microspheres have a low density, allowing them to remain
suspended in solutions for extended periods, facilitating various
experimental techniques.
- Chemical Stability: The chemical stability
of PMMA ensures that these microspheres maintain their integrity in
different environments and experimental conditions.
Applications:
- Flow Cytometry: PMMA microspheres are
employed as calibration standards in flow cytometry, allowing for the
standardization and validation of instruments used in cell analysis.
- Material Science: Researchers use PMMA
microspheres as model systems to study the behavior of colloidal
suspensions and materials at the microscale.
- Biotechnology: These microspheres
serve as tools for various biotechnological applications, including
diagnostics, immunoassays, and protein purification.
Synergistic Applications:
- Combined Strength: When the nanoparticles
and microspheres are used together, they offer a comprehensive toolkit for
researchers, addressing both nanoscale and microscale needs in a variety
of applications.
- Versatility: The combination of
these materials provides researchers with a versatile set of tools that
can be tailored to specific research goals, from nanomedicine to materials
science.
The Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Microspheres epitomize the intersection of innovation and
precision in the world of nanotechnology and materials science. As these
materials continue to pave the way for advancements in biomedicine, optics, and
materials research, the scientific community eagerly anticipates the myriad
possibilities they offer.
The synergy of nanoparticles and microspheres underscores the importance of versatility and customization in modern scientific exploration, heralding a future where microscopic components play a macroscopic role in shaping our understanding and application of materials on the nanoscale.
No comments:
Post a Comment